- Conditions
- Procedures
- Patient care
- Why choose us
- Our Doctors
- Contact
Osteoarthritis of the Shoulder
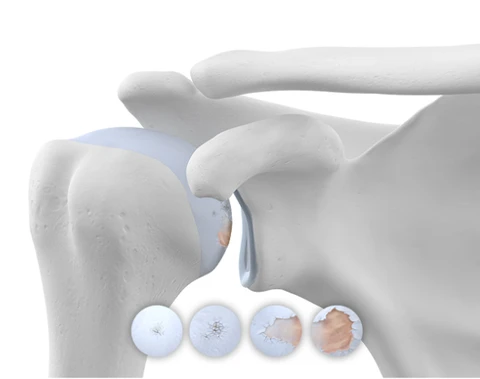
Shoulder osteoarthritis overview
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of the inflammatory condition known as arthritis. Caused by changes to the body related to age, osteoarthritis develops when protective joint cartilage begins to wear down and cause inflammation of the joints due to increased friction between bone endings. Osteoarthritis frequently develops in the shoulder due to the wear and tear we put on these important joints every day.
While osteoarthritis is not curable or reversible, it is highly manageable. The USA Spine Care team wants to help patients learn more about the conditions affecting them and the treatments available. To learn more or for answers to questions you have after reading this guide, please contact our dedicated team.
Osteoarthritis of the shoulder causes
The shoulders connect the arms to the upper body by joining the ball at the top of the arm bone to a socket in the shoulder blade that is also linked to the collar bone. We are able to perform all the movements required by the arm due to a collection of soft tissue known as the rotator cuff. Similar to other joints, friction is limited by a rubbery coating of cartilage and joint fluid.
With age, the body dries out due to natural changes we all experience. The cartilage becomes brittle and starts to wear out. The joint fluid also begins to dry up. This causes increased bone-on-bone contact and inflammation in the joints that are the hallmark of osteoarthritis. Common reasons for it to develop in the shoulders particularly include working a physical job that includes heavy lifting, performing repetitive motions for long periods of time and strenuous activities like tennis or golf.
Common symptoms of shoulder osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis-related inflammation causes symptoms that can be painful and limiting to mobility. This includes:
- Aches in the shoulder
- Pain that is described as deep within the shoulder joint
- Stiffness and limited range of motion
- A popping sensation known as crepitus
- Radiating or shooting pain down the arm in some cases
Osteoarthritis in the shoulder may be more noticeable on one side if it is more heavily used. If a stiff and aching shoulder persists for longer than a week, it is recommended to see your doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnosis for osteoarthritis in the shoulder
Diagnosing shoulder osteoarthritis should begin with a thorough examination by a physician. This will generally include a review of you and your family’s medical history, questions about your symptoms and hands-on testing to determine range of motion and identify tender spots.
Next, a doctor will often order tests to confirm osteoarthritis. Diagnostic imagery, such as an X-ray or MRI, often reveals narrowing in the shoulder joint space as well as bony growths, known as bone spurs or osteophytes, that are a common byproduct of osteoarthritis. After reaching a diagnosis of shoulder osteoarthritis, physicians will typically begin with a course of conservative treatment options.
Shoulder osteoarthritis treatment
Because osteoarthritis is not reversible, the objective of treatment is relieving symptoms and improving range of motion. This can often be successfully accomplished through nonsurgical treatment.
Common conservative treatments for osteoarthritis include:
- Rest — Limiting strain on the shoulder can lessen symptoms and slow the progression of the condition.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs — Over-the-counter medications, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help lessen pain and inflammation.
- Physical therapy — Therapeutic exercises and manual therapy can help to mobilize the joints and strengthen supporting muscles.
- Corticosteroid injections — A steroid injection in the shoulder can reduce inflammation for periods of weeks or months, allowing for the completion of physical therapy.
- Lifestyle changes — Adopting an anti-inflammatory diet as well as changing posture and movement during daily activities can both help with osteoarthritis management.
Conservative treatment can be effective and a large number of people are able to experience noticeable improvement by finding the right combination of therapies that work for them.
When to consider surgery for osteoarthritis in the shoulder
In cases of osteoarthritis, surgery generally becomes a serious consideration if there is operable damage to the shoulder that has not responded to a full course of conservative treatment.
Surgical procedures can range from minimally invasive techniques to “clean” out an arthritic shoulder by removing bone spurs and other damaged tissue to performing a full or partial shoulder joint replacement. Replacement, or arthroplasty, is only recommended if the shoulder joint has become more seriously damaged due to inflammation from osteoarthritis. In this form of surgery, a surgeon will remove a portion of the shoulder joint and implant an artificial replacement joint.
Osteoarthritis of the shoulder treatment at USA Spine Care & Orthopedics
The highly skilled medical team at USA Spine Care team has decades of combined experience helping patients with shoulder osteoarthritis find lasting relief. We have a comprehensive range of effective treatment options, including conservative and surgical therapies. Contact us today for more information.
Call toll free 1- 866-249-1627.
